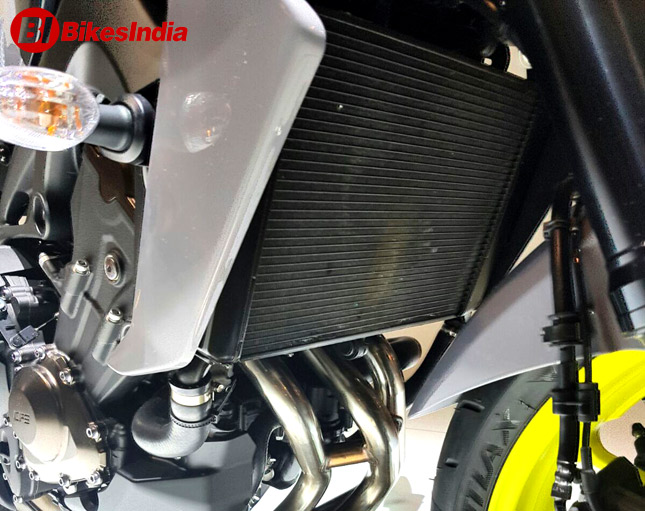
 Radiators are no longer a rare sight on motorcycles; earlier it was only four wheelers we used to witness “Radiators” but with the evolution of motorcycle industry and production of big capacity engines the Radiators have become a common sight. The internal combustion engines which are tend to generate high amount of heat during the combustion process needs to be addressed. The high revving engines are equally responsible to generate enormous amount of heat which if not taken care of could lead to failure of the engine. Therefore, to address the problem and to manage the heat dissipated from the engine various types of “Cooling Systems” have been introduced. Out of these cooling systems, the Air Cooling, Oil Cooling and the Liquid Cooling systems have been the most common in the automobile industry.
Radiators are no longer a rare sight on motorcycles; earlier it was only four wheelers we used to witness “Radiators” but with the evolution of motorcycle industry and production of big capacity engines the Radiators have become a common sight. The internal combustion engines which are tend to generate high amount of heat during the combustion process needs to be addressed. The high revving engines are equally responsible to generate enormous amount of heat which if not taken care of could lead to failure of the engine. Therefore, to address the problem and to manage the heat dissipated from the engine various types of “Cooling Systems” have been introduced. Out of these cooling systems, the Air Cooling, Oil Cooling and the Liquid Cooling systems have been the most common in the automobile industry.Wherein the Air cooling system require increased surface area of the affected part of the engine and the cool external air, the Liquid cooling system consists of a system based on liquid (Coolant/water) to cool down the engine or to regulate the heat generated while the combustion process. The liquid cooling system mainly consists of Radiator. The function of the radiator is to ensure a close contact of the hot coolant coming out of the engine with the outside air, so as to ensure high rates of heat transfer from coolant to air.
RELATED ARTICLE: Air Cooled Vs Liquid Cooled Motorcycle Engines
A radiator consists of an upper tank, core, and a lower tank. It works on the principle of counter flow heat exchanger. A drain pipe is provided in the lower tank. Hot coolant from engine enters into the radiator at the top and is cooled by cross flow air, while flowing down the radiator. The coolant collects in the collector tank from where it is pumped for engine cooling.
There are two basic types of radiator cores, the tubular and the cellular type. Out of these the tubular is the more common type of radiator used. It is further classified depending upon the shape of fins around the tubes, which is meant to increase the area for heat transfer from coolant to cooling air. Both the core types and the tubes are made from the thinnest material possible. The tubes are made from 0.1mm to 0.3mm sheet, and the fins are made from 0.1mm thick material.
RELATED ARTICLE: Motorcycle Engine Coolant- all you need to know
The materials of the radiator must be resistant to corrosion, possess high thermal conductivity and should have adequate strength. Aluminum is mostly used due to weight and cost considerations. Some radiators have a plastic tank with aluminum cores.
The size of the radiator must be adequate to remove the heat which approximately equal to the heat energy utilized for producing power in engine. Alternatively the radiator size is matched to displacement of the volume of the engine. The frontal area of the radiator is kept minimum, which may be achieved by making the core thicker and accommodating more core material into the same volume without increasing the air resistance.
For heavy duty applications, radiator shutters are also used. These are automatically controlled by means of compressed air taken in from the brake system. Shutter control mechanism is installed with the upper hose of the cooling system. Depending upon the coolant temperature from the engine, the shutter control mechanism causes the shutter to open or close. Here the Thermostat system of the engine plays vital role, however, the same system remains integrated part of cooling system by virtue of diagnosing the overall temperature.
READ ALSO: Oil Cooling Mechanism In Bikes Explained
With the help of Thermostat the Fan present right behind the Radiator can be controlled. Based on the inputs from the Thermostat, whenever it is required additional air flow on the radiator to get the hot coolant cooled down more efficiently the fan/fans get automatically switched on. The fan/fans present on the cooling system depends on the requirement are directly connected to the system and governed by the inputs received from the Thermostat.
It is very important to take care of the Radiator on the whole to ensure the life of the engine and its overall performance. You can do this by always checking and maintaining the coolant level in the radiator, by checking the proper functioning of the Radiator Fan and by being vigilant about any leakage in the Radiator.
By: Rishath Suresh











