We all are aware that motorcycle engines come in different capacities and configurations, but not everyone bothers to go deep down and analyze which bike has what type of engine. So what follows here is an analysis of the types of engine configurations and their characteristics put together in simple words, so that you don't need to be someone like Jeremy Burgess to understand.
A basic entry level commuter motorbike usually has a single cylinder unit, as the segment is mostly preferred by people who commute often and have fuel efficiency as their primary concern. A single cylinder bike ticks all the check boxes for an average man, ranging from maintenance costs to affordability.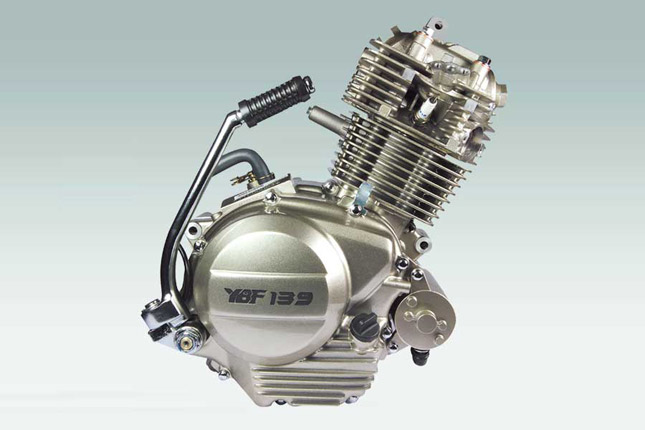
The most interesting part and the reason behind this write-up, happens when additional cylinders get added to a single pot engine. This results in the following engine configurations:
1. The Inline
This is the most widely used configuration of multi cylinder engines. An inline engine is an engine that has its cylinders arranged in one row. It may have two to six cylinders depending on the requirement. For example, a Kawasaki Ninja 300 has an inline twin whereas a BMW K1600 GTL has an inline six cylinder engine onboard.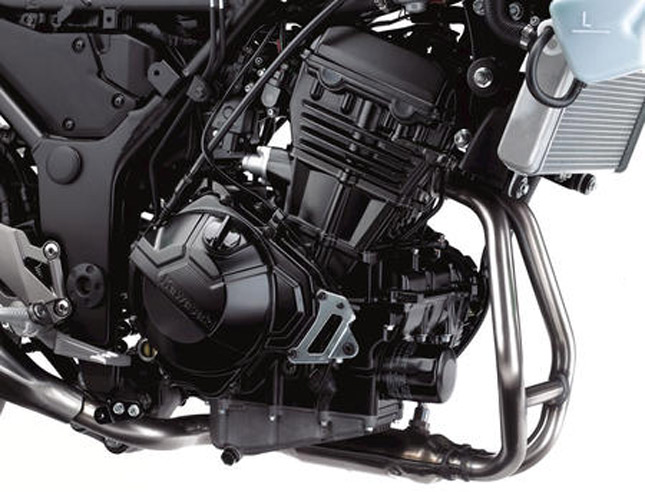
Inline engines are easier to manufacture because, the cylinder bank and crankshafts can be built from a single cast metal. It also requires fewer cylinder head and camshafts. However, Inline four is the most widely used configuration, because the engine can be built in a smaller size with multiple cylinders without affecting the ability to fit on a compact chassis. Inline fours are mostly used for sport bikes that require a wider bore and a shorter stroke, in order to accelerate at very high rpm's.
The British marquee Triumph has a legacy of making much more compact Inline three motors. Triumph believes that this gives their bikes an upper hand in terms of overall weight distribution and agility. The triple has the refinement of an inline four along with the chunky torque of an inline two, making it a mix of both worlds.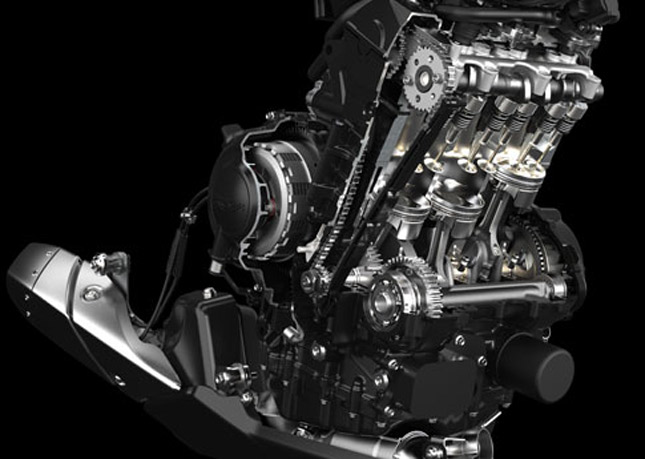
2. V Type
As the name suggests, cylinders and pistons are aligned in two separate banks, so that they appear to be in a "V" shape when viewed from the outside. Engines are generally more compact than inline engines with cylinders of the same dimensions and number. This effect increases with the number of cylinders in the engine. It helps in reducing the overall length and weight of the engine. The V engines are only built with even number of cylinders in modern times. V twin engines are the most used engines, in motorcycles. Cruisers come shod of V twins because the Stroke length can be longer without increasing the overall height of the engine. This is done because a cruiser must have a very healthy amount of torque and a long stroke engine can do the magic for the Cruisers.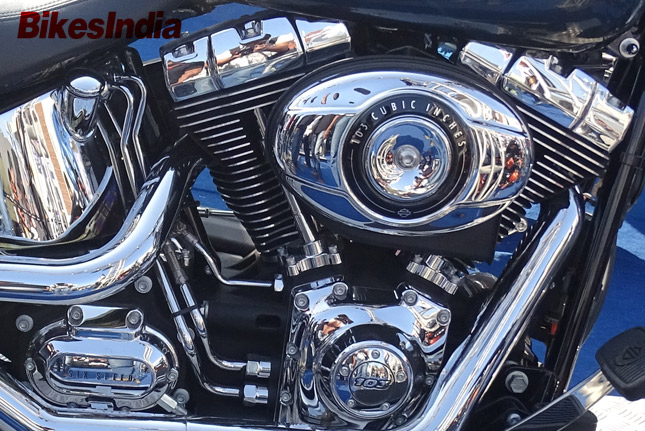
Some racing machines make use of V4 engines, because it can be coupled to a compact chassis aiding to a better handling compared with the inline four counterparts. For example, Honda's MotoGP bike RC213V uses a V4, compared to the inline four used on Yamaha's YZR M1. The Ducati Desmosedici is known for its V type configuration and they also showed their potential at MotoGP circuits especially with their superior top speed.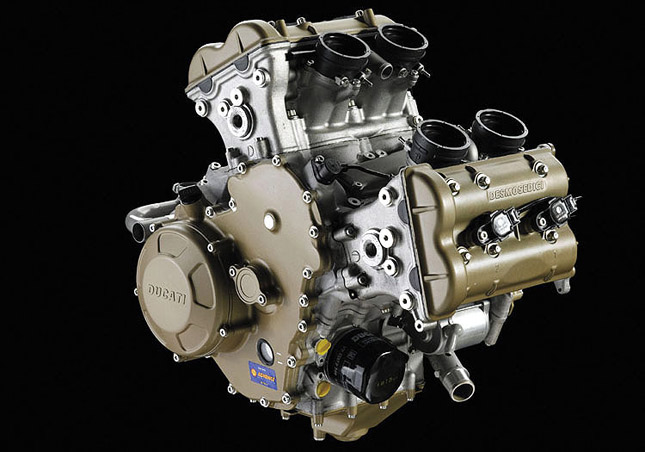
Generally the V is formed in a way that it is vertical to the axis of the bike. However, a special type of V engine is used by the Italian manufacturer "Moto Guzzi". They make bikes having horizontally opposed V engines having a longitudinal crankshaft orientation and the engine's cylinder heads projecting on either side of the bike. For example, Moto Guzzi California.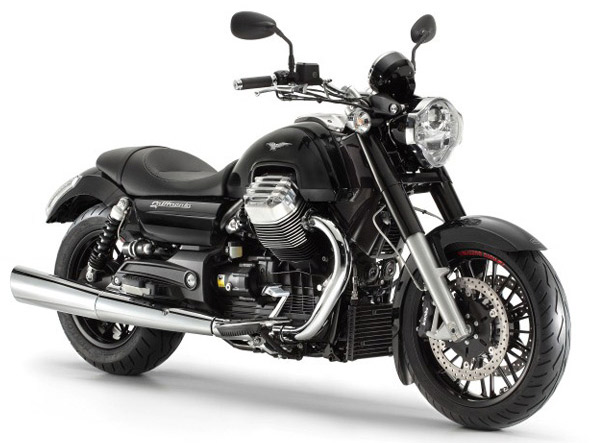
3. Boxer
The Boxer engine was first patented by German Engineer Karl Benz in 1896. The engine was then vastly equipped in production BMW Motorcycles (BMW R32) since 1923. The engine has cylinders arranged in two banks on either sides of a single crankshaft, thus the name Boxer. Boxer twin engines are the ones vastly used on BMW motorcycles. The current lineup of BMW Motorrad has motorcycles equipped with Boxer twins. For example, the BMW R1200 GS is the most successful model in production with a boxer twin engine.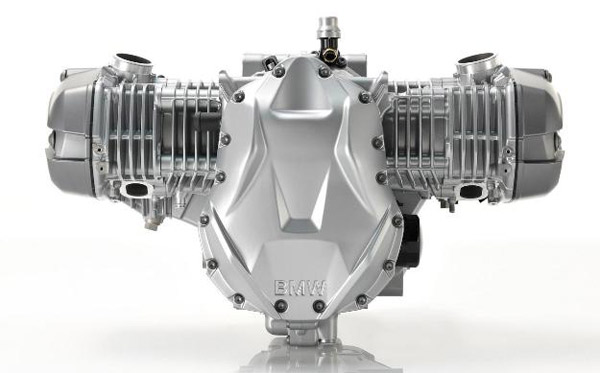
4. W Type
The two following configurations are not used in the production motorcycles. A W type engine is a combination of two V engines. It's often called as Double V engine, because of its structural appearance. The W type engine is used in the iconic Hypercar Bugatti Veyron. It uses a W16 engine, which has two V8's combined on a common crankshaft.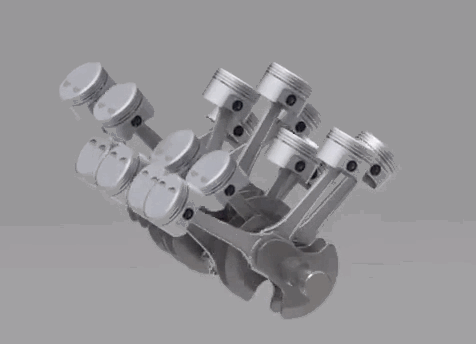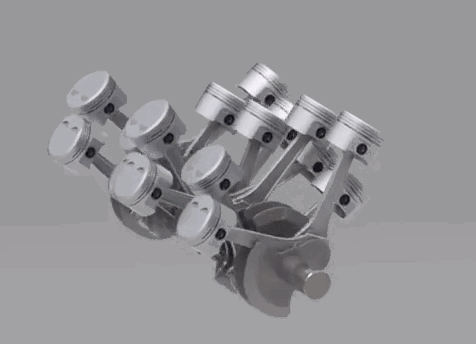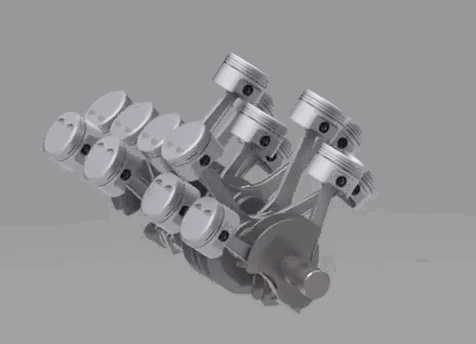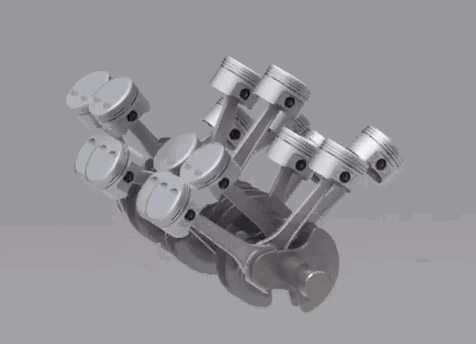 5. Wankel
5. Wankel
The Wankel engine is a type of Internal Combustion engine that uses a rotary design to convert the pressure into rotating motion. The four-stroke cycle occurs in a moving combustion chamber between the inside of an oval shaped cylinder, and a rotor that is similar to a triangle with sides that are somewhat flatter. This type wasn't much used in production motorcycles, except for the Suzuki RE5 which had a 497cc motor produced between 1974 and 1976.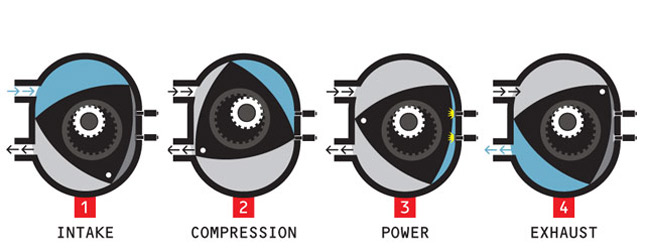 By: Aravind Rb
By: Aravind Rb
A basic entry level commuter motorbike usually has a single cylinder unit, as the segment is mostly preferred by people who commute often and have fuel efficiency as their primary concern. A single cylinder bike ticks all the check boxes for an average man, ranging from maintenance costs to affordability.

*** A basic Single cylinder motorcycle engine
The most interesting part and the reason behind this write-up, happens when additional cylinders get added to a single pot engine. This results in the following engine configurations:
1. Inline
2. V type
3. Boxer
4. W Type
5. Wankel
Now let's have a detailed description of individual engine configuration.2. V type
3. Boxer
4. W Type
5. Wankel
1. The Inline
This is the most widely used configuration of multi cylinder engines. An inline engine is an engine that has its cylinders arranged in one row. It may have two to six cylinders depending on the requirement. For example, a Kawasaki Ninja 300 has an inline twin whereas a BMW K1600 GTL has an inline six cylinder engine onboard.

*** Inline twin engine of the Kawasaki Ninja 300
Inline engines are easier to manufacture because, the cylinder bank and crankshafts can be built from a single cast metal. It also requires fewer cylinder head and camshafts. However, Inline four is the most widely used configuration, because the engine can be built in a smaller size with multiple cylinders without affecting the ability to fit on a compact chassis. Inline fours are mostly used for sport bikes that require a wider bore and a shorter stroke, in order to accelerate at very high rpm's.

*** Piston and Crankshaft arrangement of an Inline four cylinder engine (Yamaha R1 CP4)
The British marquee Triumph has a legacy of making much more compact Inline three motors. Triumph believes that this gives their bikes an upper hand in terms of overall weight distribution and agility. The triple has the refinement of an inline four along with the chunky torque of an inline two, making it a mix of both worlds.

*** The Legendary Inline three engine of Triumph Daytona 675
2. V Type
As the name suggests, cylinders and pistons are aligned in two separate banks, so that they appear to be in a "V" shape when viewed from the outside. Engines are generally more compact than inline engines with cylinders of the same dimensions and number. This effect increases with the number of cylinders in the engine. It helps in reducing the overall length and weight of the engine. The V engines are only built with even number of cylinders in modern times. V twin engines are the most used engines, in motorcycles. Cruisers come shod of V twins because the Stroke length can be longer without increasing the overall height of the engine. This is done because a cruiser must have a very healthy amount of torque and a long stroke engine can do the magic for the Cruisers.

*** V twin engine of a Harley Davidson
Some racing machines make use of V4 engines, because it can be coupled to a compact chassis aiding to a better handling compared with the inline four counterparts. For example, Honda's MotoGP bike RC213V uses a V4, compared to the inline four used on Yamaha's YZR M1. The Ducati Desmosedici is known for its V type configuration and they also showed their potential at MotoGP circuits especially with their superior top speed.

*** V4 engine of Ducati Desmosedici RR
Generally the V is formed in a way that it is vertical to the axis of the bike. However, a special type of V engine is used by the Italian manufacturer "Moto Guzzi". They make bikes having horizontally opposed V engines having a longitudinal crankshaft orientation and the engine's cylinder heads projecting on either side of the bike. For example, Moto Guzzi California.

*** Inverted V twin of Moto Guzzi California
3. Boxer
The Boxer engine was first patented by German Engineer Karl Benz in 1896. The engine was then vastly equipped in production BMW Motorcycles (BMW R32) since 1923. The engine has cylinders arranged in two banks on either sides of a single crankshaft, thus the name Boxer. Boxer twin engines are the ones vastly used on BMW motorcycles. The current lineup of BMW Motorrad has motorcycles equipped with Boxer twins. For example, the BMW R1200 GS is the most successful model in production with a boxer twin engine.

*** Boxer twin engine of a BMW R1200GS
4. W Type
The two following configurations are not used in the production motorcycles. A W type engine is a combination of two V engines. It's often called as Double V engine, because of its structural appearance. The W type engine is used in the iconic Hypercar Bugatti Veyron. It uses a W16 engine, which has two V8's combined on a common crankshaft.
 5. Wankel
5. Wankel The Wankel engine is a type of Internal Combustion engine that uses a rotary design to convert the pressure into rotating motion. The four-stroke cycle occurs in a moving combustion chamber between the inside of an oval shaped cylinder, and a rotor that is similar to a triangle with sides that are somewhat flatter. This type wasn't much used in production motorcycles, except for the Suzuki RE5 which had a 497cc motor produced between 1974 and 1976.
 By: Aravind Rb
By: Aravind Rb











